Know the difference between kbps and kBps!
Know these terms:
1. ISP - Internet Service Provider
2. kbps - Kilobits per second
3. kBps - Kilobytes per second
4. mbps - Megabits per second
5. mBps - Megabytes per second
4. mbps - Megabits per second
5. mBps - Megabytes per second
Know the following conversions:
8 bits (b) = 1 byte (B)
1024 bytes (B) = 1 kilobyte (kB)
1024 kilobytes (kB) = 1 megabyte (mB)
1024 megabyte (mB) = 1 gigabyte (gB)
1024 gigabyte (gB) = 1 terabyte (tB)
...
...
But you are shocked to see the result of the download speed displayed on your computer. It is way less than the speed promised by your ISP!
There may be three reasons why this can happen.
Reason 1:
The ISP is cheating you. Well, if this is the case, we cannot do much. Change your ISP!
Reason 2:
Reason 2:
The data transfer speed of the website is less than the speed of your internet connection. We are not worried about this. So, let us see the third one.
Reason 3:
You probably have read kbps/mbps as kBps/mBps. Yes!
ISPs normally display internet speeds offered by them in kbps/mbps. E.g.: 20 mbps (i.e. 20 megabits per second)
Your computer normally displays internet speeds in kBps/mBps. E.g.: 2.5 mBps (i.e. 2.5 megabytes per second)
Above speeds of 20 mbps and 2.5 mBps are same. This is because
8 bits = 1 byte,
which means that 8 megabits = 1 megabyte,
which means that 20 megabits = 2.5 megabytes.
So, whenever you see the speeds offered by ISPs in kbps, you can quickly know the speeds as displayed by your computer by dividing it by 8.
For e.g., if your ISP has displayed the internet speed as 4 mbps, you have to divide it by 8, which is 0.5 mBps, which is the speed as displayed by your computer.
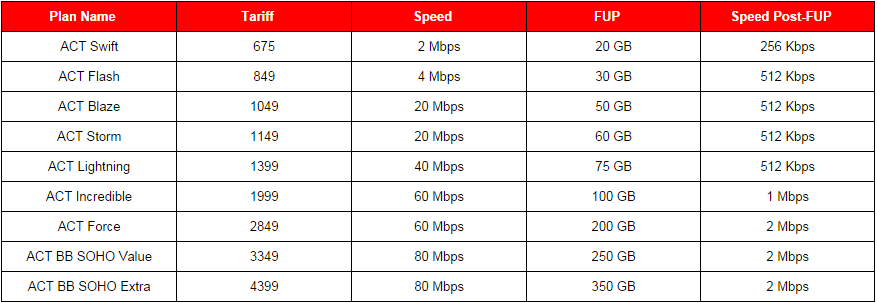
Prices charged by one of the ISPs for different internet speeds:
ISPs normally display internet speeds offered by them in kbps/mbps. E.g.: 20 mbps (i.e. 20 megabits per second)
Your computer normally displays internet speeds in kBps/mBps. E.g.: 2.5 mBps (i.e. 2.5 megabytes per second)
Above speeds of 20 mbps and 2.5 mBps are same. This is because
8 bits = 1 byte,
which means that 8 megabits = 1 megabyte,
which means that 20 megabits = 2.5 megabytes.
So, whenever you see the speeds offered by ISPs in kbps, you can quickly know the speeds as displayed by your computer by dividing it by 8.
For e.g., if your ISP has displayed the internet speed as 4 mbps, you have to divide it by 8, which is 0.5 mBps, which is the speed as displayed by your computer.
Prices charged by one of the ISPs for different internet speeds:
In case of the above ISP, speeds in terms of mBps would be:
ACT Swift = 2 mbps/8 = 0.25 mBps
ACT Flash = 4 mbps/8 = 0.5 mBps
ACT Force = 60 mbps/8 = 7.5 mBps
So, if you have a movie of 1 gB (1 gigabyte) to be downloaded, and your internet speed is 20 mbps or 2.5 mBps (both speeds are same), you can calculate the time to be downloaded as follows:
Convert the file size to the terms in which internet speed is denoted, i.e. 1 gB = 1024 mB
Therefore, file size in terms of mB = 1024
Internet speed in terms of mB = 2.5
So, time required to download the movie = 1024/2.5 = 409.6 seconds = 6.82 minutes
If you have any doubts/clarifications/suggestions, post a comment below!
Sources:
ACT Swift = 2 mbps/8 = 0.25 mBps
ACT Flash = 4 mbps/8 = 0.5 mBps
ACT Force = 60 mbps/8 = 7.5 mBps
So, if you have a movie of 1 gB (1 gigabyte) to be downloaded, and your internet speed is 20 mbps or 2.5 mBps (both speeds are same), you can calculate the time to be downloaded as follows:
Convert the file size to the terms in which internet speed is denoted, i.e. 1 gB = 1024 mB
Therefore, file size in terms of mB = 1024
Internet speed in terms of mB = 2.5
So, time required to download the movie = 1024/2.5 = 409.6 seconds = 6.82 minutes
If you have any doubts/clarifications/suggestions, post a comment below!
Sources:
Wikipedia - Data rate units
Image 2 - ACT Fibernet